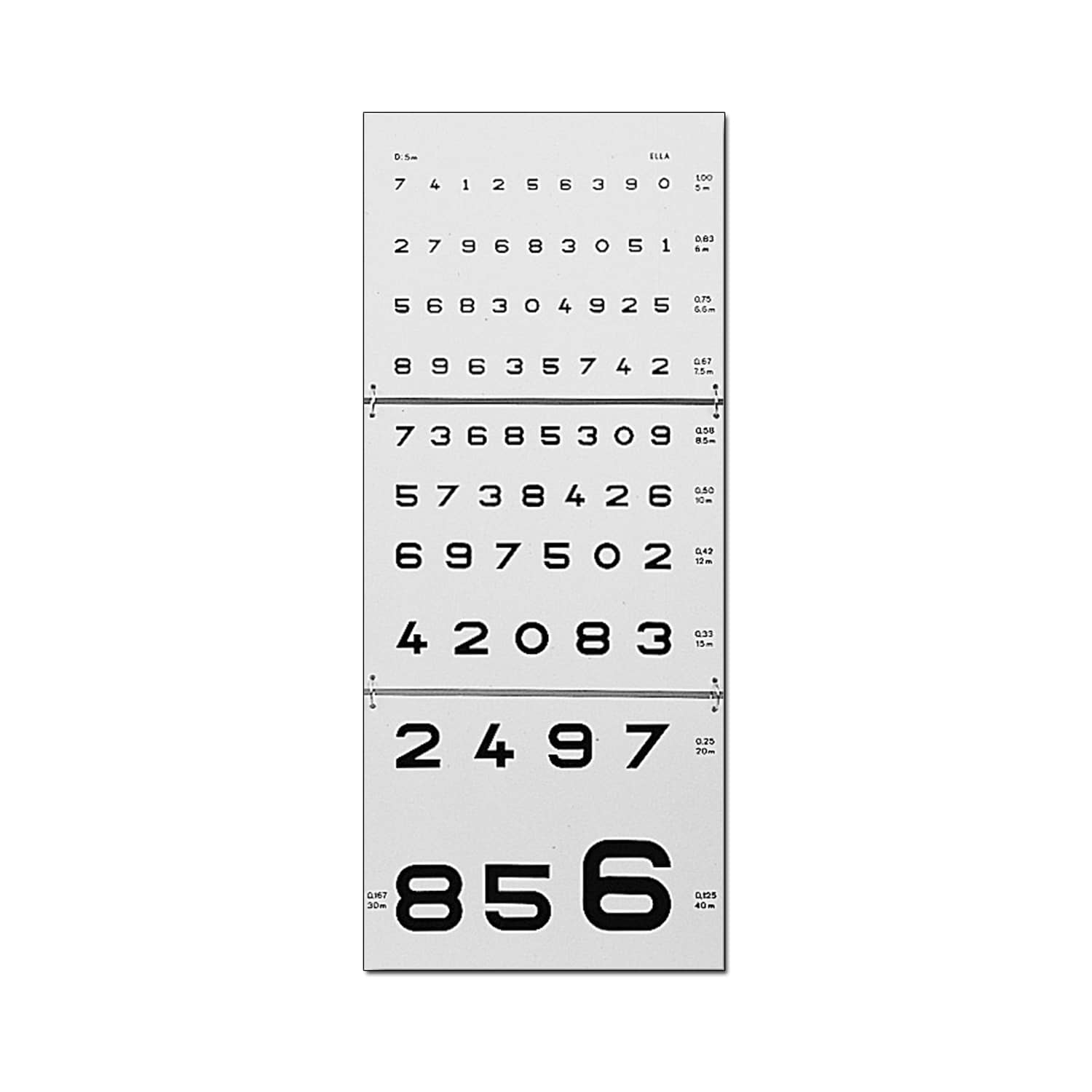
“Numbers” Reading Scale
59,00€ excluding tax
“Numbers” Reading Scale
- Direct reading at 5 m
- 1 / 10th of visual acuity per line
- Wall
- SKU: 88877-01
- Categories: Acuity scales
Additional information
How to measure visual acuity using a reading scale?
For measure sharpness visual with a reading scale, the Snellen scale is generally used, which is the most commonly used. Here are the steps to perform this measurement:
- Positioning : The patient is placed at a specific distance from the optometric chart, usually at a distance of 6 meters (20 feet) for the standard Snellen scale. This distance is important because the scale is designed to measure visual acuity at this distance.
- Reading letters : The optometry chart has several rows of letters or symbols of decreasing size. The patient is asked to read the letters in each row, starting at the top of the board and gradually working down.
- Recording of results : The eye care professional writes down the letters correctly identified by the patient. Each row of the table is associated with a specific level of visual acuity. For example, if the patient can correctly read the letters in the row at the fourth level from the top, this indicates a visual acuity of 4/10.
- Visual acuity calculation : visual acuity is usually expressed as a fraction, where the numerator represents the distance the patient is from the chart (usually 6 meters) and the denominator represents the smallest letter size the patient can read. For example, a visual acuity of 6/6 means the patient can read at 6 meters what the average person can read at 6 meters, while a visual acuity of 6/12 means the patient can read at 6 meters what that the average person can read at 12 meters.
I'Snellen scale therefore makes it possible to assess the sharpness of an individual's vision by comparing their ability to read the letters of the table at a given distance with the average ability of a person with normal vision. This makes it possible to determine if visual correction is necessary and to prescribe appropriate glasses or contact lenses if necessary.
How to use the Parinaud reading scale?
I'Parinaud reading scale, also called the Parinaud scale or near scale, is used to assess near visual acuity. It is specifically designed to measure near vision and is often used during eye exams to assess an individual's ability to read small print up close.
Here's how to use Parinaud's reading scale:
- Positioning : the patient is placed at a specific distance from the optometric chart, usually at a standard reading distance of 40 centimeters (or a distance recommended by the ophthalmologist).
- Reading characters : Parinaud's table presents several rows of characters of different sizes, going from the largest at the top to the smallest at the bottom. The patient is asked to read the characters in each row, starting at the top of the table and gradually working down.
- Recording of results : the vision professional notes the characters correctly identified by the patient. Each row of the table is associated with a specific level of near visual acuity.
- Calculation of near visual acuity : Near visual acuity is usually expressed as a number, which represents the size of the characters read compared to a standard size. For example, if the patient can read the characters in row 1 (largest) of the chart, this indicates a visual acuity of close to 1.00. If the patient can only read the characters in row 4 (smaller), this indicates a visual acuity of close to 0.40.
I'Parinaud scale is used to assess near vision, which is essential for activities such as reading, writing, and other tasks that require clear near vision. It helps determine if reading glasses or other visual aids are needed to improve the patient's near vision.
How to use the Monoyer reading scale?
I'Monoyer reading scale is an optometry chart used to assess distance visual acuity. It is generally used during ophthalmological examinations to measure an individual's ability to read smaller and smaller characters at a certain distance. Here's how to use the Monoyer Reading Scale:
- Positioning : the patient is placed at a specific distance from the optometric chart, usually at a standard distance of 6 meters (or a distance recommended by the ophthalmologist). This distance is essential for the measurements to be carried out correctly.
- Reading characters : Monoyer's table presents several rows of characters of different sizes, going from the largest at the top to the smallest at the bottom. The patient is asked to read the characters in each row, starting at the top of the table and gradually working down.
- Recording of results : the vision professional notes the characters correctly identified by the patient. Each row of the table is associated with a specific level of distance visual acuity.
- Distance visual acuity calculation : Distance visual acuity is usually expressed as a fractional number, for example 20/20. The first number represents the distance the patient is standing from the standard distance of 6 meters (for example, if the patient is standing 3 meters away and correctly reads the row corresponding to 6 meters, the visual acuity would be recorded as 6/3). The second number represents the distance at which a person with normal vision would be able to read the same character. Thus, a visual acuity of 20/20 means that the patient can read at 6 meters what a person with normal vision should read at 6 meters.
I'Monoyer reading scale assesses distance visual acuity and determines whether the patient requires glasses or other visual corrections to improve distance vision. It is widely used in routine eye examinations and vision checks to measure the sharpness and clarity of a patient's vision.